
The size and shape of the dots are not important, only the color.
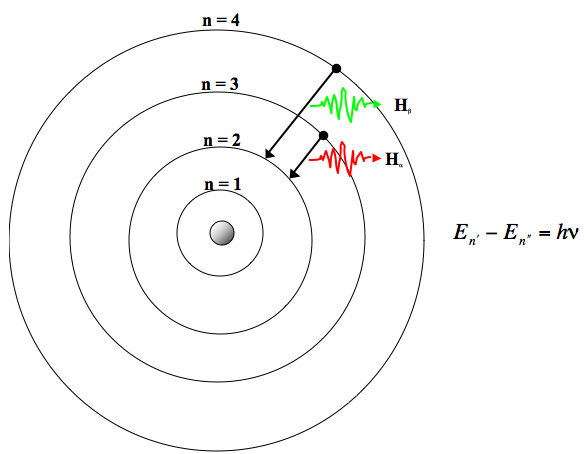
Run the default simulation experiment by pressing the "on" button of the light source (which is a red button on the ray gun).Open the Java applet Hydrogen Atom Model Applet.Elliptical orbits are also possible.īohr atom model fails to explain Zeeman effect (magnetic effects on atomic spectra) and Stark effect (electrical effects on atomic spectra). There is no logical explanation of considering the electron orbits only as circular orbits. It cannot be extended for atoms with more than one electron.īohr atom model fails to explain the fine structure of the spectral lines.īohr's theory fails to account for the variations of intensities of the The Bohr model is applicable to hydrogen and hydrogenic atoms only. Some of important limitations are as follows: Radiation emitted or selectively absorbed, yet the model has many limitations. Limitations of Bohr Atom ModelĪlthough Bohr atom model correctly predicts the gross features, specially the frequency/wavelength of These spectral lines are called emission lines. Thus, we can see that as per Bohr atom model, the various lines in atomic spectra of hydrogen are produced when electrons jump from higher energy state to lower energy state and photons of appropriate energy or frequency are emitted. However, if E i < E f, then the electron must absorb a photon to go to higher energy state. If E i > E f, then a photon is emitted in the process. (3) Quantum concept of radiant energy:- It states that whenever an electron makes a transition from one stable specified non-radiating orbit, it emits/absorbs a radiation photon whose energy is equal to the energy difference between the initial and final states. The second postulate signifies the quantization of angular momentum. The number n is generally known as the principal quantum member. Multiple of h/2π, where h is the planck's constant. Nucleus only in those orbits for which its angular momentum is some integer It states that the electron revolves around the (2) Bohr's quantum condition:- Bohr's second postulateĭefines the stable orbits. These states are called the stationary states of the atom. The first postulate of Bohr signifies that each atom has certain definite stable states in which it can exist and each possible state has definite total energy. The electron revolves around the nucleus in certain specified circular orbits without the emission of radiant energy. (1) An atom consists of a tiny, central part called nucleus, in which whole positive charge and almost whole mass of an atom is concentrated. Postulates of Bohr Atom Modelīohr atom model is based on the following three postulates:
Bohr argued that although classical electromagnetic theory is extremely successful in explanation phenomena at macroscale but it needs a radial modification to explain the structure of atoms and relation of atomic structure to atomic spectra.īohr combined classical and early quantum, concepts and proposed a modified nuclear model of atom, nowadays know as Bohr's atom model.

In 1913, Niels Bohr made certain modifications in Rutherford's atom model by adding the ideas of newly developing quantum hypothesis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
